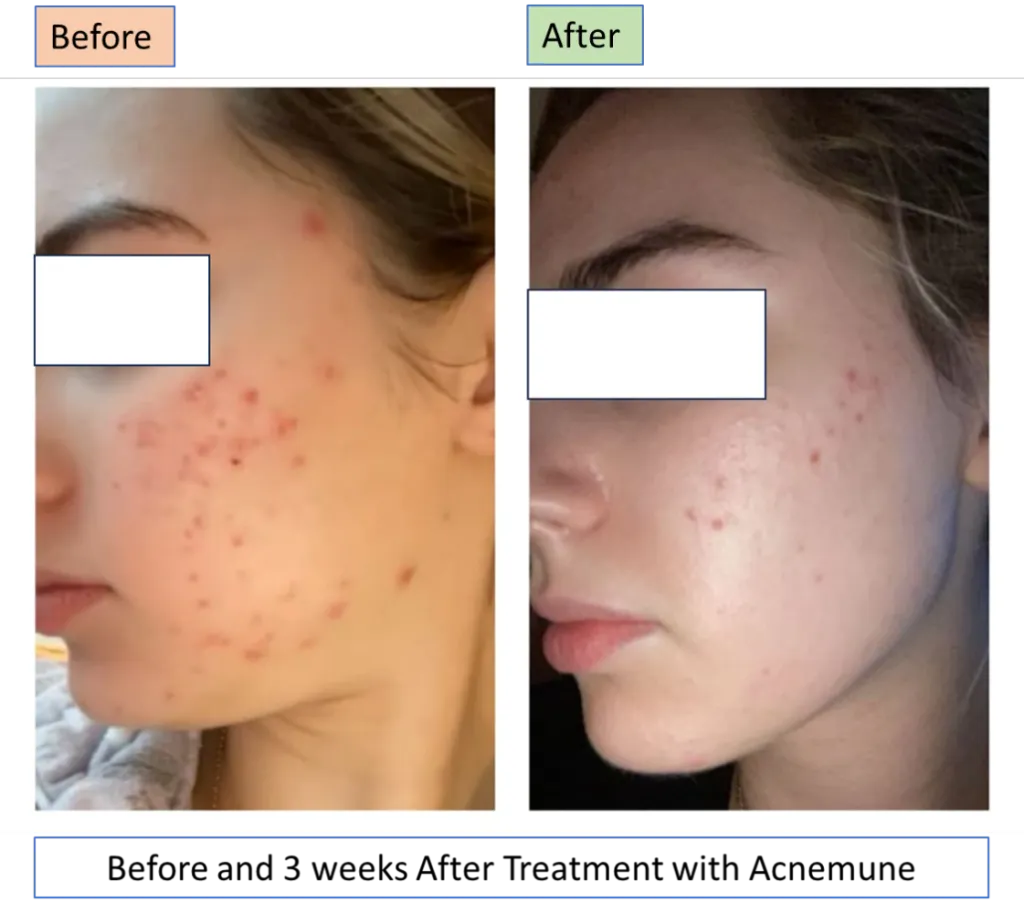


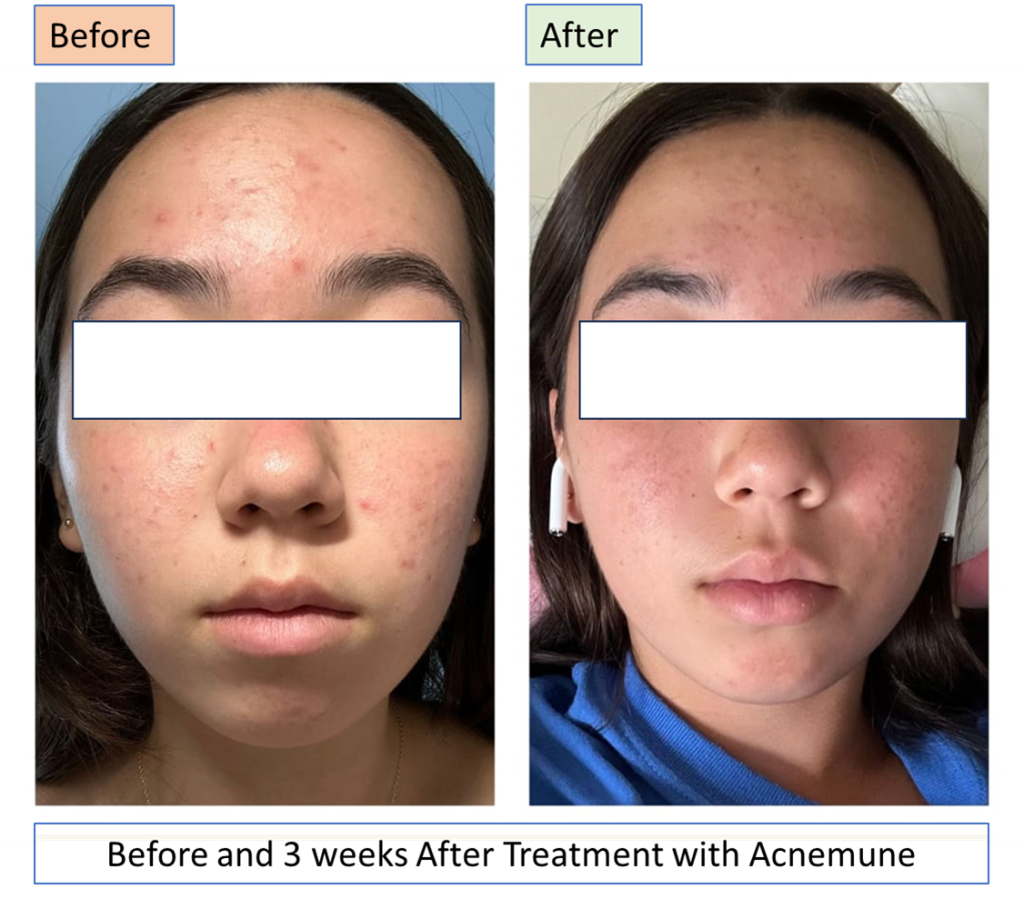
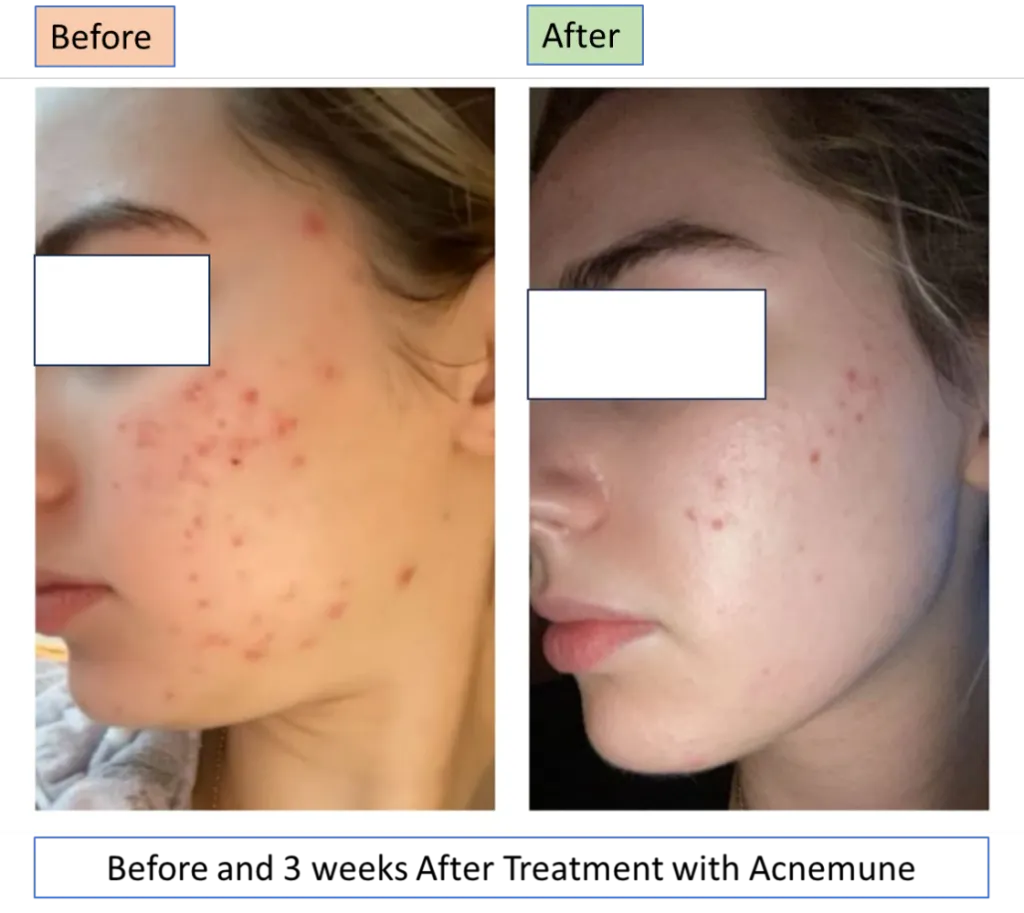
To celebrate the effectiveness of Acnemune, we offer a 100% discount on your second order if you provide quality pictures of before, during, and after your treatment period of 3-4 weeks. This offer is available only to the first 50 customers who purchase Acnemune from the date of the online shopping launch.
How to reach us
Any questions or concerns? Please contact us at care@acnemune.com
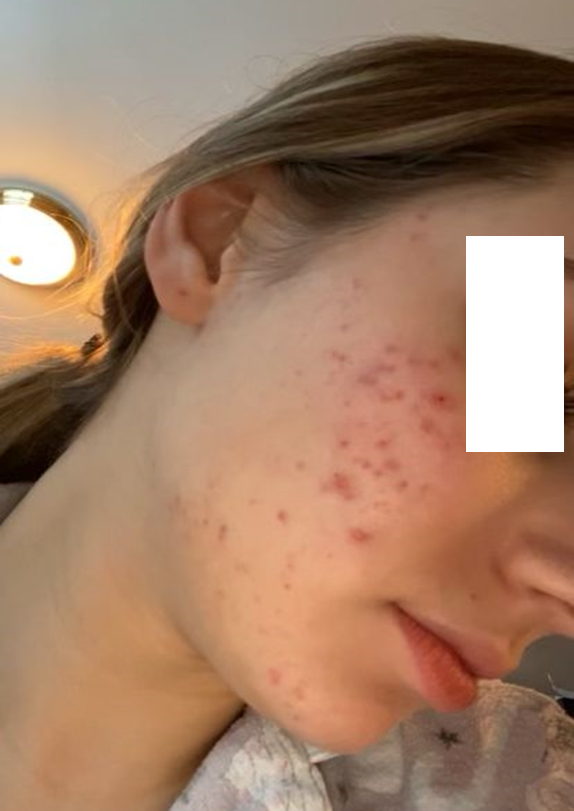
Acne (scientifically also knows as acne vulgaris) is a skin condition in which pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, appear on the face, chest and back. Pimples containing pus are called pustules, and those without pus are called papules. Blackheads and whiteheads are together known as comedones. Severe cases of acne can cause cysts and nodules to form under the skin and can result in scarring, which can be permanent. Acne is classified based on the type of lesions (comedones, papules, pustules, etc.) and severity.
Most experts agree there are four main causes of acne:
Excess oil, clogging of hair follicles by oil and dead skin, bacteria, and inflammation
General causes and chain of events leading to acne:
Hair follicles with sebaceous glands, mostly in the face, increase in size and cause a so-called whitehead, and once the plug opens to the surface and darkens it produces a so-called blackhead, which is not caused by dirt but by an excess of bacteria and oil. Further blockages and continued inflammation deep inside the hair follicles that are in contact with the sebaceous glands cause the appearance of lumps that look like cysts under the skin.
Factors that can cause or make acne worse include:
Hormonal changes, i.e. increase in androgens that cause the sebaceous glands to grow in size and produce more sebum.
Some medications that contain testosterone, corticosteroids or lithium.
Certain diets rich in carbohydrates.
Stress may make an already formed acne worse.
Comparing Acnemune with Other Acne prescription and over the counter treatments
Current other available Acne prescription and over the counter treatments and side effects
Over the counter treatments
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring acid produced by a yeast which is an antibacterial used as a 20% azelaic acid cream or gel twice a day.
Side effects: skin redness and minor skin irritation.
Salicylic acid may help prevent clogged hair follicles as wash-off and leave-on products. Studies have shown its effectiveness is limited.
Side effects: skin discoloration and minor skin irritation.
Prescription Treatments
Retinoids and retinoid-like drugs. Drugs that have retinoic acids or tretinoin sometimes, but not always, are effective against moderate acne, and are found as creams, gels and lotions. Some examples include tretinoin, adapalene and tazarotene. It is to be applied in the evening, beginning with three times a week, then daily, to prevent plugging of hair follicles.
Side effects: Topical retinoids increase the skin’s sun sensitivity. They can also cause dry skin and redness, especially in people with brown or Black skin. Adapalene may be tolerated best.
Antibiotics. These work by killing excess skin bacteria and reducing redness and inflammation. For the first few months of treatment, both a retinoid and an antibiotic may be used, with the antibiotic applied in the morning and the retinoid in the evening. The antibiotics are often combined with benzoyl peroxide to reduce the likelihood of developing antibiotic resistance. Examples include clindamycin with benzoyl peroxide (Benzaclin, Duac, others) and erythromycin with benzoyl peroxide (Benzamycin). Topical antibiotics alone aren’t recommended.
Evidence is not strong in support of using zinc, sulfur, nicotinamide, resorcinol, sulfacetamide sodium or aluminum chloride in topical treatments for acne.
Antibiotics. For moderate to severe acne, oral antibiotics are used to reduce bacteria. These include tetracycline (minocycline, doxycycline) or a macrolide (erythromycin, azithromycin).
Side effects: Increase the skin’s sun sensitivity. These antibiotics should be used only for the shortest time possible to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Combined oral contraceptives. Four combined oral contraceptives are approved by the FDA for acne therapy in women who also wish to use them for contraception: combination of progestin and estrogen.
Side effects: weight gain, breast tenderness and nausea. These drugs are also associated with increased risk of cardiovascular problems, breast cancer and cervical cancer.
Anti-androgen agents. The drug spironolactone (Aldactone) can be considered for women and adolescent girls, in case oral antibiotics are ineffective. They block the effect of androgen hormones on the oil-producing glands.
Side effects: breast tenderness and painful periods.
Isotretinoin. Isotretinoin (Amnesteem, Claravis, others) is a derivative of vitamin A and may be prescribed for people whose moderate or severe acne who hasn’t responded to other treatments.
Side effects: Potential inflammatory bowel disease, depression and severe birth defects. All people receiving isotretinoin must participate in an FDA-approved risk management program. And they’ll need to see their doctors regularly to monitor for side effects.
Other Acne Therapies
There are several other therapies that are either ineffective or may only work for mild cases of acne. These include, light therapy, chemical peel, drainage and extraction and steroid injections.

Et non est nisl mi vitae faucibus ut nulla amet malesuada bibendum massa vivamus tempor imperdiet posuere fusce adipiscing
Et non est nisl mi vitae faucibus ut nulla amet malesuada bibendum massa vivamus tempor imperdiet posuere fusce adipiscing sit tellus quam.

Et non est nisl mi vitae faucibus ut nulla amet malesuada.